 アブストラクト
アブストラクト| Date | December 21, 2011 |
| Speaker | Dr. Kiyoko F. Aoki-Kinoshita, Soka University |
| Title | Development of a Multiple Glycan Alignment Tool |
| Abstract |
The understanding of glycan function is important because they play significant roles within an organism such as determining blood type, participating in cellular adhesion and virus infections, etc. As such, we developed a tool for prediction of glycan recognition patterns for the purpose of elucidating glycan recognition mechanisms of glycan binding proteins. We have been developing the MCAW (Multiple Carbohydrate Alignment with Weights) algorithm for multiple glycan alignment, which can be used on glycan array data, for example, to infer glycan profiles. This algorithm has now been implemented as a tool in RINGS[1]
The MCAW algorithm is based on a method similar to ClustalW [2], which is a popular multiple amino acid sequence alignment algorithm. Figure 1 is the dynamic programming algorithm for MCAW. Q[u, v] is the glycan alignment score for u and v, which are the residue positions of each profile being compared. A (resp. B) is the number of glycans in the profile of u (resp. v). an (resp. bm) signifies the weight of glycan An (resp. Bm). w(un,vm) is the score between the sugars in positions u and v of glycans An and Bm, respectively. sons(u) (resp. sons(v)) are the child nodes of u (resp. v). M(u,v) is the mapping between the children of nodes u and v [3]. 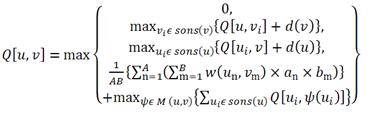 Figure 1: Dynamic programming algorithm of MCAW A MCAW tool has now been implemented in RINGS to output a multiple glycan alignment of an input data set of glycans. In the input screen, glycan structures are input in KCF format (Figure 2A). Additionally, it is possible to add weighting options when calculating the alignment score. There are options to weight the monosaccharides, anomers, non-reducing side carbon number and reducing side carbon number in the "Advanced weighting options" (Figure 2B). Presently in MCAW tool, we have confirmed the possibility of aligning up to 88 glycans. As further work, we will show diagrammatically the alignment result, and the results of MCAW will be used in an improved version of a tool to compute glycan profiles using a probabilistic model [4,5,6]. Thus, our study will become an important basis for further research in glycoinformatics, including the analysis of glycan profiles, glycan score matrices and probabilistic models. [1] Akune, Y., Hosoda, et al. OMICS. 14(4):475-86, 2010. [2] Thompson, J.D., et al. Nucleic Acids Research, Vol. 22, No. 22, 4673-4680, 1994. [3] Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F. GLYCOME INFORMATICS: methods and applications. Taylor and Francis, Ltd. 2009. [4] Ueda, N., Aoki-Kinoshita, K. F., et al., IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 17(8), 1051-1064, 2005. [5] Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F., et al. Bioinformatics, 22:e25-e34, 2006. [6] Hashimoto, K., Aoki-Kinoshita, et al., Proc. KDD, 177-186, 2006. |